Alkylated branched poly(β-amino esters) demonstrate strong DNA encapsulation, high nanoparticle stability and robust gene transfection efficacy†
Abstract
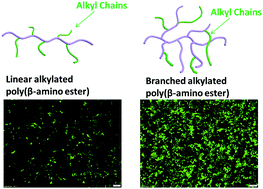
A branched poly(β-amino ester) with numerous alkyl chains (BPA) is designed and synthesized as a safe and efficient non-viral vector. The branching and hydrophobicity synergistically endow BPA with tight DNA condensation, high polyplex stability in serum, high cellular uptake and ultimately robust gene transfection efficiency, largely superior to its linear counterpart (LPA). Our results demonstrate that branching matters for gene delivery by hydrophobic gene vectors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...