Length-dependent intracellular bundling of single-walled carbon nanotubes influences retention†
Abstract
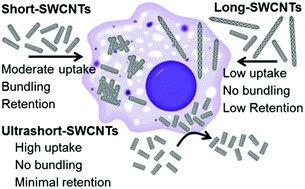
Single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) are increasingly being investigated for biomedical imaging, sensing, and drug delivery. Cell types, cellular entry mechanisms, and SWCNT lengths dictate SWCNT uptake, subsequent intracellular trafficking, and retention. Specialized immune cells known as macrophages are capable of two size-dependent entry mechanisms: endocytosis of small particles (diameter < 200 nm) and phagocytosis of large particles (diameter > 500 nm). In comparison, fibroblasts uptake particles predominantly through endocytosis. We report dependence of cellular processing including uptake, subcellular distribution, and retention on the SWCNT length and immune cell-specific processes. We chose SWCNTs of three different average lengths: 50 nm (ultrashort, US), 150 nm (short) and 500 nm (long) to encompass two different entry mechanisms, and noncovalently dispersed them in water, cell culture media, and phosphate buffer (pH 5) with bovine serum albumin, which maintains the SWCNT optical properties and promotes their cellular uptake. Using confocal Raman imaging and spectroscopy, we quantified cellular uptake, tracked the intracellular dispersion state (i.e., individualized versus bundled), and monitored recovery as a function of SWCNT lengths in macrophages. Cellular uptake of SWCNTs increases with decreasing SWCNT length. Interestingly, short-SWCNTs become highly bundled in concentrated phase dense regions of macrophages after uptake and most of these SWCNTs are retained for at least 24 h. On the other hand, both US- and long-SWCNTs remain largely individualized after uptake into macrophages and are lost over a similar elapsed time. After uptake into fibroblasts, however, short-SWCNTs remain individualized and are exocytosed over 24 h. We hypothesize that aggregation of SWCNTs within macrophages but not fibroblasts may facilitate the retention of SWCNTs within the former cell type. Furthermore, the differential length-dependent cellular processing suggests potential applications of macrophages as live cell carriers of SWCNTs into tumors and regions of inflammation for therapy and imaging.
- This article is part of the themed collections: RSC papers by NanoEngineering for Medicine and Biology 2018 Speakers and Carbon Nanostructures in Biology and Medicine


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...