Nickel–gold bimetallic monolayer colloidal crystals fabricated via galvanic replacement as a highly sensitive electrochemical sensor†
Abstract
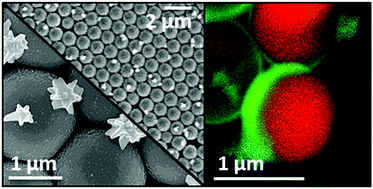
Bimetallic Ni–Au monolayer colloidal crystals (MCCs) were fabricated by galvanic replacement of Ni monolayers with Au salt. The influence of Au concentration used in the galvanic replacement solutions on the morphology and structure of the resulting Ni–Au surface is studied. It was found that the use of monolayer colloidal crystals, which display cohesive structure formations across the monolayer, results in the galvanic replacement reaction occurring more evenly over the surface when compared to the thin film counterpart. The fabricated devices were analyzed under alkaline conditions using chronoamperometric techniques to detect glucose concentrations ranging between 20 μM and 10 mM. The optimum Ni–Au MCC substrate was produced using 0.1 mM Au salt solution and showed a very low experimental detection limit of 14.9 μM and a calculated sensitivity of 506 μA mM−1 cm−2, which was ∼3 times larger than that of the plain Ni MCC substrate. The Ni–Au MCC substrate also showed minimal current response changes in the presence of common physiological contaminants, thus being a highly selective electrochemical glucose sensor.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...