Minimum hyaluronic acid (HA) modified magnetic nanocrystals with less facilitated cancer migration and drug resistance for targeting CD44 abundant cancer cells by MR imaging†
Abstract
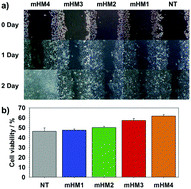
We report minimal amount of hyaluronic acid (HA) conjugated magnetic nanocrystals (mHMs) for targeted imaging of CD44 abundant breast cancer cells via MRI. These mHMs lead to less induced cancer migration and drug resistance, which is distinct from conventional approaches using nanoplatforms (imaging or therapeutic systems) that are completely covered with HA. To synthesize mHMs, magnetic nanocrystals (MNCs), as MRI contrast agents, were encapsulated mostly with polysorbate 80 (P80, non-reactive to HA) and partially with aminated P80 (reactive to HA). This system enabled conjugation of an immensely diminished amount of HA onto MNCs. While these nanoparticles maintained good CD44 targeted imaging efficacy, they also showed no cytotoxicity and colloidal stability. We varied the HA ratios on an equal amount of MNCs and identified that when more HA was attached on nanoparticles, there was more facilitated cancer migration and drug resistant potentials. We chose the lowest amount of HA conjugated mHMs (mHM1) and demonstrated that mHM1 selectively diagnosed tumor regions in vivo. We believe that the technique described herein can be applied to various applications using HA to detect CD44 abundant cancer cell lines and offer a basis to understand the interaction between the cellular response and surface modification of nanoparticles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...