Borophene and defective borophene as potential anchoring materials for lithium–sulfur batteries: a first-principles study†
Abstract
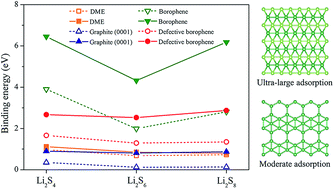
Lacking effective anchoring materials to suppress the severe shuttle effect is a longstanding issue hindering the development of lithium–sulfur (Li–S) batteries. In this work, a first-principles study is carried out to investigate the potential of borophene and defective borophene, which have high ionic conductivity and adsorbent ability, as anchoring materials for Li–S batteries. Borophene is found to exhibit ultra-high adsorption energies towards lithium polysulfides, but the material facilitates the decomposition of Li–S clusters, leading to an undesirable sulfur loss during battery cycling. For this reason, borophene is not an ideal anchoring material for Li–S batteries. On the contrary, defective borophene is found to show moderate adsorption energies ranging from 1 to 3 eV, which not only effectively anchors lithium polysulfides to suppress the shuttle effect, but also keeps their cyclic structures undecomposed. In addition, defective borophene exhibits a metallic characteristic during the whole reaction process, ensuring the lithium polysulfides be easily charged back and not accumulate on the anchoring materials. Given these advantages, it is expected that defective borophene is a promising anchoring material, leading to a suppressed shuttle effect and enhanced capacity retention for Li–S batteries.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...