An integrated approach towards the fabrication of highly efficient and long-term stable perovskite nanowire solar cells†
Abstract
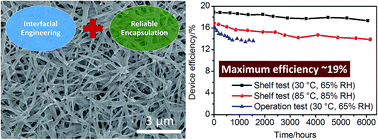
Although organic–inorganic lead halide perovskite nanowires (NWs) have shown great potential in a wide range of device applications, their relatively low performance and insufficient stability represent major bottlenecks for their further development. In this study, we present an integrated approach to achieve highly efficient and long-term stable methyl ammonium lead iodide (MAPbI3) perovskite NW solar cells by combining a 4-(1,3-dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)-N,N-diphenylaniline (N-DPBI)-doped poly{[N,N′-bis(2-octyldodecyl)-1,4,5,8-naphthalene diimide-2,6-diyl]-alt-5,5′-(2,2′-bithiophene)} (P(NDI2OD-T2)) polymeric film as the electron transport layer (ETL) with an atomic-layer-deposited Al2O3-based film as the encapsulation layer. Our results indicate that N-DPBI doping can not only improve the electron extraction capability by minimizing resistive losses, but also improve the surface coverage of the P(NDI2OD-T2) ETL on the MAPbI3 NW layer. With this n-doped ETL, a remarkable power conversion efficiency (PCE) up to 18.83% is achieved, which represents the highest PCE ever reported for perovskite NW solar cells. Importantly, taking advantage of the high charge carrier mobility of MAPbI3 NWs (0.01 cm2 V−1 s−1), the large-area NW devices with an active area of 5.04 cm2 also deliver a high PCE up to 15.25%. More encouragingly, the encapsulated NW devices exhibit excellent long-term stability, retaining ∼92% of their initial efficiency after being exposed to the ambient atmosphere for more than 6000 hours. The encapsulated NW devices still remain fairly stable (∼20% loss in PCE) even after ∼1500 hours of continuous operation under AM1.5G sunlight irradiation in the ambient atmosphere. The approaches demonstrated herein can not only offer a very promising strategy for realizing high-performance and long-term stable perovskite NW solar cells, but also pave the way for future developments of perovskite NW-based optoelectronic devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...