Brønsted base site engineering of graphitic carbon nitride for enhanced photocatalytic activity†
Abstract
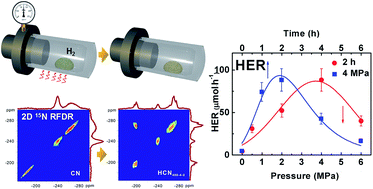
Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) is a promising two-dimensional polymeric photocatalyst in the field of solar energy conversion. In the past few years many modifications of g-C3N4 have been studied extensively; however, the difficulty in obtaining detailed structural information both on its intrinsic covalent interactions and surrounding bonding environments largely restricts the rational design and development of inherent structure-controlled g-C3N4 based photocatalysts and fundamental understanding of their mechanistic operations. Herein, we demonstrate a high-pressure hydrogenation treatment method for g-C3N4 and introduce 1D 13C and 15N and 2D 15N Radio Frequency-driven Dipolar Recoupling (RFDR) solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy for identifying the structural information and surrounding hydrogen-bonding environment of treated g-C3N4 samples. The surface Brønsted base sites of g-C3N4 samples can be tuned systematically through changing the treatment conditions. We find that the terminal isolated –NH2 and the hydrogenated nitrogen species in treated g-C3N4 samples seem to be the origin of their improved activities for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution and favor the enhancement of light harvesting and carrier transport. The as-prepared HCN400-4-2 sample treated at a pressure of 4 MPa and a temperature of 400 °C for 2 h in a hydrogen atmosphere displays the highest H2 evolution reaction (HER) activity, which is over 26 times higher than that of pristine g-C3N4.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...