Selective electrochemical CO2 reduction to CO using in situ reduced In2O3 nanocatalysts†
Abstract
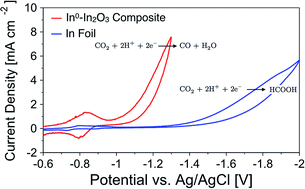
Both metallic indium and indium oxide electrocatalysts typically have high selectivity for producing formate via the electrochemical reduction of CO2 in aqueous media. It has been suggested that under highly negative potentials, i.e. potentials typically sufficient to reduce indium oxide to In0, the native oxide layer on metallic indium or indium oxide particles is not reduced to In0 when exposed to CO2-saturated electrolytes. This meta-stable oxide layer is crucial in the mechanism for producing formate via the two-electron, two-proton reduction of CO2; however it prevents the catalysis from occurring on In0. Herein, we report that electrochemically reducing In2O3 nanocatalysts in Ar-saturated electrolytes in situ, prior to CO2 exposure, will remove this metastable oxide layer and create an In0–In2O3 composite. This In0–In2O3 composite material changes the selectivity and is able to electrochemically reduce CO2 to CO with near 100% selectivity at relatively low overpotentials (c.a. −1.0 V vs. Ag/AgCl). We attribute the change in selectivity to the direct exposure of In0 to CO2 in solution that typically does not exist due to the native oxide layer that forms on In metal. In addition, we observed that the first electron-transfer step to form the surface adsorbed intermediates is highly reversible on the In0–In2O3 composite; however it is irreversible on an In foil electrode. We also report the utilization of Substrate Generation-Tip Collection Scanning Electrochemical Microscopy (SG-TC SECM) to measure the production of CO as a function of applied potential. This technique allows for the collection of CO in situ during the voltammetry experiment as it is produced on the catalytic electrode, which results in accurate potential dependent measurements of CO production.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...