A bifunctional NiCoP-based core/shell cocatalyst to promote separate photocatalytic hydrogen and oxygen generation over graphitic carbon nitride†
Abstract
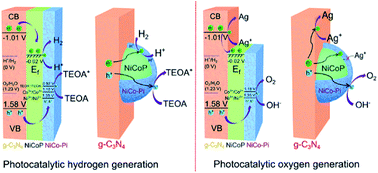
Developing suitable cocatalysts is crucial to promoting photocatalytic hydrogen and oxygen generation using solar energy. Herein, non-precious NiCoP-based cocatalysts were synthesized by a facile solid-state phosphorization reaction, and coupled with metal-free graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) for photocatalytic reactions. It was revealed that NiCoP-based nanoparticles exhibited a core/shell structure, where the NiCoP core was surrounded by amorphous-like nickel cobalt phosphate (NiCo–Pi) shell. The detailed spectroscopic and electrochemical studies demonstrated that NiCoP cores behaved as the active sites for the photocatalytic reductive half-reaction, and NiCo–Pi shells could serve as the active sites for the photocatalytic oxidative half-reaction. As a consequence, the improved surface reaction rate through the bifunctional NiCoP-based cocatalyst, as well as the enhanced charge separation efficiency, cooperatively boosted the separate photocatalytic hydrogen and oxygen generation in the presence of appropriate sacrificial reagents. The apparent quantum efficiency for hydrogen generation over the NiCoP@NiCo–Pi/g-C3N4 photocatalyst can reach 9.4% at 420 nm, which is one of the best values for noble-metal-free g-C3N4-based photocatalysts. To our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of the NiCoP-based cocatalyst to promote both photocatalytic hydrogen and oxygen generation, which is expected to pave a new way to exploit efficient bifunctional cocatalysts for overall water splitting.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...