Hypergolic fuels based on water-stable borohydride cluster anions with ultralow ignition delay times†
Abstract
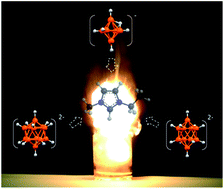
In bipropulsion systems, hypergolic ionic liquids with B–H groups, as promising alternatives to toxic hydrazine-based fuels, can improve propulsion performance. A series of borohydride cluster-based salts with excellent hydrolytic and thermal stabilities (Td > 200 °C), and the highest density (1.18 g cm−3) of any known borohydride hypergolic ionic liquids were prepared. Upon contact with white fuming nitric acid or N2O4, these new salts have ultra-fast ignition delay times (as low as 1 ms), which is a superior ignition performance. Theoretical studies were employed in order to understand their high stability and good ignition performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...