Carbon nanoparticles of Chinese ink-wrapped natural loofah sponge: a low-cost three-dimensional electrode for high-performance microbial energy harvesting†
Abstract
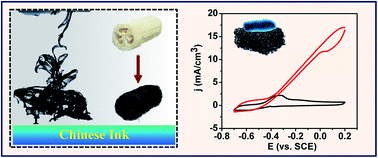
Three-dimensional (3D) electrodes have been intensively investigated as high-performance electrodes to harvest microbial energy in bioelectrochemical systems (BESs). However, the fabrication of low-cost high-performance 3D electrodes is still a great challenge. Herein, we reported a new highly conductive and biocompatible 3D electrode by simply coating natural loofah sponge (LS) with low-cost Chinese ink (CI) that has been used for writing and drawing for thousands of years. A high current density of 16.3 ± 0.5 mA cm−3 was achieved by the as-prepared Chinese ink-coated loofah sponge (CI-LS), which is close to that of the 3D electrode produced from the carbonized LS and equals those of most of the available materials in the current state of research. This high current density is attributed to the open macroporous structure of the LS as well as high conductivity and good biocompatibility of the carbon nanoparticle coating layers. The performance of the CI-LS depended strongly on the type of CI used as the conductive coating material. Besides, the resulting bioelectrode displayed promising stability, which outperformed other 3D electrodes based on synthetic sponges. Considering the low-cost and facile fabrication, this CI-LS 3D electrode has promising potential for high-performance and cost-effective BESs on a large scale.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...