Enhanced solvent-free selective oxidation of cyclohexene to 1,2-cyclohexanediol by polyaniline@halloysite nanotubes†
Abstract
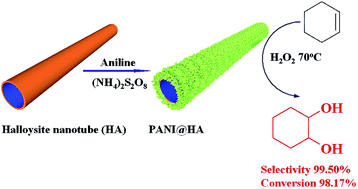
One-dimensional polyaniline@halloysite (PANI@HA) nanotubes with enhanced selective oxidation activity of cyclohexene are fabricated by employing aniline (ANI) chemical polymerization on halloysite nanotubes in situ. By facilely controlling the doping acid, acidity, and ANI/HA weight ratio during the fabrication, PANI with a controllable doping degree, redox state, and content is grown on halloysite nanotubes. The cyclohexene selective oxidation result shows that PANI@HA nanotubes are effective catalysts in a solvent-free reaction system with H2O2 as the oxidant, and their catalytic activity relies on the doping acid, acidity, and ANI/HA weight ratio in the fabrication. PANI@HA synthesized with HCl as a doping acid to condition the acidity at 1 M and 2.04 ANI/HA weight ratio (PANI@HA/1 M/2.04-HCl) demonstrates highest catalytic activity (98.17% conversion and 99.50% selectivity to 1,2-cyclohexanediol). The cyclohexene selective catalytic activity matches well with the PANI doping degree in PANI@HA. In addition, the optimal reaction condition is 20 mg catalyst, 2.5 mL H2O2, 70 °C, and 24 h. Furthermore, PANI@HA/1 M/2.04-HCl exhibits superior dihydroxylation activity toward 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene and cycling performance with 99.11% conversion and 96.92% selectivity to 1,2-cyclohexanediol after five cycles. The CV of PANI@HA indicates that the cyclohexene selective oxidation is attributed to a reversible redox reaction of PANI in PANI@HA for catalytic decomposition of H2O2.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...