In situ directional formation of Co@CoOx-embedded 1D carbon nanotubes as an efficient oxygen electrocatalyst for ultra-high rate Zn–air batteries†
Abstract
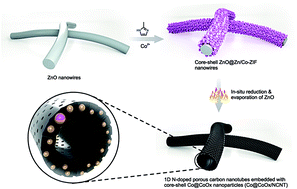
In this work, we demonstrate a “three birds one stone” strategy for preparing 1D N-doped porous carbon nanotubes embedded with core–shell Co@CoOx nanoparticles (Co@CoOx/NCNTs) from bimetallic ZnO@Zn/Co-ZIF nanowires. The ZnO nanowires played three roles: (i) ZnO acted as a template for 1D metal–organic framework (MOF) growth, (ii) in situ evaporation of Zn during pyrolysis prevented the aggregation of the carbon framework and benefited the formation of hierarchical pores, and (iii) the excess oxygen species released from ZnO in situ reacted with metallic cobalt nanoparticles during pyrolysis, leading to the configuration of a Co@CoOx core–shell structure. The as-prepared 1D Co@CoOx/NCNTs exhibited excellent oxygen reduction reaction performance, including a high kinetic current (4.6 times better compared to 20 wt% Pt/C at 0.7 V), a low Tafel slope of 80 mV dec−1, outstanding stability, and strong tolerance to CH3OH crossover. The assembled Zn–air batteries with Co@CoOx/NCNTs yielded high open-circuit voltage (1.52 V), superior stability (over 100 h of operation), and unprecedented rate performance that ranged from 1 to 500 mA cm−2, while existing batteries have never achieved a galvanostatic discharge current density larger than 300 mA cm−2. Such exceptional rate capability was ascribed to the formation of a uniform interconnected nanotube network, facilitated electron transport, and an enlarged electrochemically accessible surface area in the unique 1D porous tubular structure.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...