Quadruple metal-based layered structure as the photocatalyst for conversion of carbon dioxide into a value added carbon monoxide with high selectivity and efficiency†
Abstract
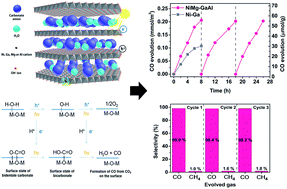
Metal-based layered structures are promising structures for use as photocatalysts, but ones that are capable of enabling a complete conversion of carbon dioxide (CO2) into a value added carbon monoxide (CO) are still limited. In this paper, a quadruple metal-based layered structure, composed of aluminium (Al), gallium (Ga), magnesium (Mg), and nickel (Ni), is reported which allows the photocatalytic conversion of CO2 into CO with a high selectivity close to 100% in the presence of water. The shifted oxidation states on the Ni and Mg ions than bivalent states lead to an increment in electronegativity for their neighboring oxygen (O) while the Ga and Al ions maintain their trivalent states, thereby enabling the O to adsorb a high amount of CO2. Furthermore, the quadruple metal-based layered structure without any use of scavengers is proven to give an approximately two-fold increase in photocatalytic activity compared to those with bi or triple metal-based structures.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...