Vanadia–titania multilayer nanodecoration of carbon onions via atomic layer deposition for high performance electrochemical energy storage†
Abstract
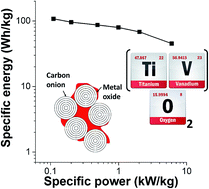
Atomic layer deposition has proven to be a particularly attractive approach for decorating mesoporous carbon substrates with redox active metal oxides for electrochemical energy storage. This study, for the first time, capitalizes on the cyclic character of atomic layer deposition to obtain highly conformal and atomically controlled decoration of carbon onions with alternating stacks of vanadia and titania. The addition of 25 mass% TiO2 leads to expansion of the VO2 unit cell, thus greatly enhancing lithium intercalation capacity and kinetics. Electrochemical characterization revealed an ultrahigh discharge capacity of up to 382 mA h g−1 of the composite electrode (554 mA h g−1 per metal oxide) with an impressive capacity retention of 82 mA h g−1 (120 mA h g−1 per metal oxide) at a high discharge rate of 20 A g−1 or 52C. Stability benchmarking showed stability over 3000 cycles when discharging to a reduced potential of −1.8 V vs. carbon. These capacity values are among the highest reported for any metal oxide system, while in addition, supercapacitor-like power performance and longevity are achieved. At a device level, high specific energy and power of up to 110 W h kg−1 and 6 kW kg−1, respectively, were achieved when employing the hybrid material as anode versus activated carbon cathode.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...