Exploring the potential of ionic bipolar diodes for chemical neural interfaces†
Abstract
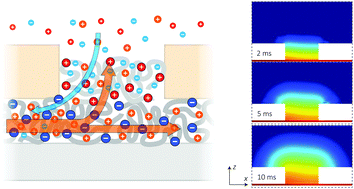
Technology interfaces which can imitate the chemically specific signaling of nervous tissues are attractive for studying and developing therapies for neurological disorders. As the signaling in nervous tissue is highly spatiotemporal in nature, an interfacing technology should provide local neurotransmitter release in the millisecond range. To obtain such a speed, the neurotransmitters must be stored close to the release point, while avoiding substantial passive leakage. Here we theoretically investigate whether ionic bipolar diodes can be used for this purpose. We find that if a sufficiently large reverse potential is applied, the passive leakage can be suppressed to negligible levels due to the high local electric field within the bipolar diode. The influences of various design parameters are studied to determine the optimal design and operation. Finally, the delivery speed of the component is evaluated using time-dependent simulations, which show that the release of neurotransmitters to physiologically relevant concentrations can be achieved in less than 10 ms. Altogether, the results suggest that ionic bipolar diodes constitute a highly attractive technology for achieving high speed low leakage addressable delivery circuits for neural interfaces.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...