Mechanism of gelation in low-concentration aqueous solutions of silver nitrate with l-cysteine and its derivatives
Abstract
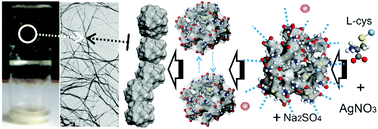
We discuss the results of experimental studies of the processes of gelation in aqueous solutions of silver nitrate with L-cysteine and its derivatives. We focus on understanding what determines if these small molecules will self-assemble in water at their extremely low concentration to form a gel. A mechanism of gel formation in a cysteine–silver solution (CSS) is proposed. The analysis of the results indicates that filamentary aggregates of a gel network are formed via interaction of NH3+ and C(O)O− groups that belong to neighboring silver mercaptide (SM) aggregates. In turn, formation of sulphur–silver bonds between silver mercaptide molecules is responsible for self-assembling these molecules into SM aggregates which can be considered as supramonomers. Free polar groups located on the surfaces of the aggregates can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, which explains the unique ability of CSS hydrogels to trap water at low concentrations of low-molecular-weight hydrogelators.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...