Diffusion in systems crowded by active force-dipole molecules
Abstract
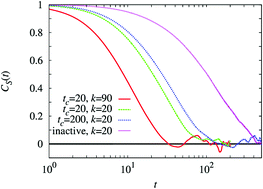
Experimental studies of systems containing active proteins that undergo conformational changes driven by catalytic chemical reactions have shown that the diffusion coefficients of passive tracer particles and active molecules are larger than the corresponding values when chemical activity is absent. Various mechanisms have been proposed for such behavior, including, among others, force dipole interactions of molecular motors moving on filaments and collective hydrodynamic effects arising from active proteins. Simulations of a multi-component system containing active dumbbell molecules that cycle between open and closed states, a passive tracer particle and solvent molecules are carried out. Consistent with experiments, it is shown that the diffusion coefficients of both passive particles and the dumbbells themselves are enhanced when the dumbbells are active. The dependence of the diffusion enhancement on the volume fraction of dumbbells is determined, and the effects of crowding by active dumbbell molecules are shown to differ from those due to inactive molecules.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...