Aromatic ionene topology and counterion-tuned gelation of acidic aqueous solutions†
Abstract
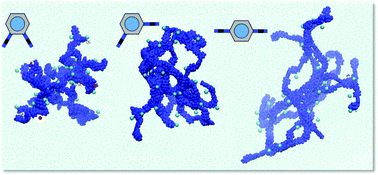
Unusual gelation of acidic solutions was achieved using polycations bearing quaternary ammonium moieties. These ionene polymers are based on a disubstituted phenylene dibenzamide core, which allows the construction of different topomers (i.e. ortho-1, meta-2 and para-3). The topology of the polymers was found to play a key role on their aggregation behaviour both in pure water and in a variety of aqueous acidic solutions leading to the formation of stable acidic gels. Specifically, ortho-1 showed superior gelation ability than the analogues meta-2 and para-3 in numerous solutions of different pH and ionic strengths. Lower critical gelation concentrations, higher gel-to-sol transition temperatures and faster gelation were usually observed for ortho-1 regardless the solvent system. Detailed computational molecular dynamic simulations revealed a major role of the counterion (Cl−) and specific polymer⋯polymer interactions. In particular, hydrogen bonds, N–H⋯π interactions and intramolecular π–π stacking networks are distinctive in ortho-1. In addition, counterions located at internal hydration regions also affect to such polymer⋯polymer interactions, acting as binders and, therefore, providing additional stability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...