Carbide-derived carbon beads with tunable nanopores from continuously produced polysilsesquioxanes for supercapacitor electrodes†
Abstract
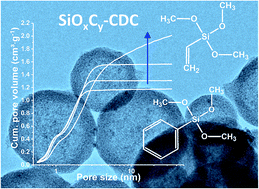
The MicroJet reactor technique is an excellent continuous method to produce spherical and homogeneous organically modified silica (ORMOSIL) particles in a large scale (10–15 g min−1). We applied this method to manufacture polyorganosilsesquioxanes with different ratios of phenyl and vinyl functional groups, which were later pyrolyzed to obtain silicon oxycarbides. Such polymer-derived ceramic (PDC) materials are highly suited as precursor for carbide-derived carbon (CDC) synthesis. Chlorine etching of PDC at high temperatures removed silicon and oxygen, yielding the formation of nanoporous carbon. Pure poly(phenyl-silsesquioxane) spheres lost their shape during the thermal process by undergoing further condensation reactions. Yet, the spherical shape was conserved during thermal processing after adding vinyl functionalities. The ratio of vinyl and phenyl functionalities controlled the pore structure and the total CDC yield, enabling an increase from 2 mass% to 22 mass%. The total pore volume varied between 1.3-2.1 cm3 g−1 and the specific surface area between 2014–2114 m2 g−1. The high surface area and large pore volume makes these materials attractive for high power supercapacitor electrodes. The specific capacitance of the best sample at low rates in 1 M tetraethylammonium tetrafluoroborate in acetonitrile was 116 F g−1 (at 5 mA g−1) and still 80 F g−1 at very high rates (at 100 A g−1).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...