Facile preparation and highly efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution of novel CuxNiy nanoalloy/graphene nanohybrids
Abstract
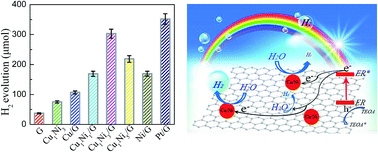
Graphene nanohybrids loaded with CuxNiy bimetallic nanoalloys (CuxNiy/G) were obtained via a facile co-reduction process. The composition and structure of the CuxNiy/G were characterized by X-ray diffraction, high resolution transmission electron microscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The results showed that, besides composition, the size and morphology of CuxNiy particles on the graphene were different from those of Cu particles or Ni particles on graphene by the same preparation process. Furthermore, with eosin Y and rose bengal (ER) as co-sensitizers, and the CuxNiy bimetallic nanoalloy as the co-catalyst, the photocatalytic activity of hydrogen evolution over the CuxNiy/G increased and reached 5.05 mmol g−1 h−1 when the molar ratio of Cu2+ to Ni2+ was 1 : 3. Compared with that of pure graphene (G), its activity was enhanced by up to 8.2 times. It was also higher than those of Cu or Ni loaded G, and even comparable to that of Pt loaded graphene under the same conditions. The higher activity of the CuxNiy/G could be attributed to the small size effect and special morphology of the CuxNiy alloy, fast interfacial electron transfer and synergic interaction in the CuxNiy/G system. Therefore, the CuxNiy bimetallic nanoalloy could act as a cheap and highly efficient noble metal-free cocatalyst for enhancing photocatalytic activity for hydrogen production over graphene-based photocatalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...