Formylation or methylation: what determines the chemoselectivity of the reaction of amine, CO2, and hydrosilane catalyzed by 1,3,2-diazaphospholene?†
Abstract
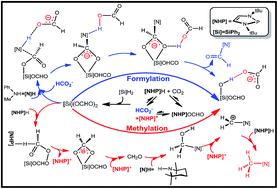
DFT computations have been performed to gain insight into the mechanisms of formylation/methylation of amines (e.g. methylaniline (1a)/2,2,4,4-tetramethylpiperidine (2a)) with CO2 and hydrosilane ([Si]H2, [Si] = Ph2Si), catalyzed by 1,3,2-diazaphospholene ([NHP]H). Different from the generally proposed sequential mechanism for the methylation of amine with CO2, i.e. methylation proceeds via formylation, followed by further reduction of formamide to give an N-methylated amine, the study characterized a competition mechanism between formylation and methylation. The chemoselectivity originates from the competition between the amine and [NHP]H hydride to attack the formyloxy carbon of [Si](OCHO)2 (the insertion product of CO2 into [Si]H2). When the attack of an amine (e.g.1a) wins, the transformation affords formamide (1b) but would otherwise (e.g.2a) result in an N-methylated amine (2c). The reduction of formamide by [Si]H2 or [NHP]H is highly unfavorable kinetically, thus we call attention to the sequential mechanism for understanding the methylation of amine with CO2. In addition, the study has the following key mechanistic findings. The activation of CO2 by [NHP]H establishes an equilibrium: [NHP]H + CO2 ⇄ [NHP]OCHO ⇄ [NHP]+ + HCO2−. The ions play catalytic roles to promote formylation via HCO2− or methylation via[NHP]+. In 1a formylation, HCO2− initiates the reaction, giving 1b and silanol byproducts. However, after the initiation, the silanol byproducts acting as hydrogen transfer shuttles are more effective than HCO2− to promote formylation. In 2a methylation, [NHP]+ promotes the generation of the key species, formaldehyde and a carbocation species (IM17+). Our experimental study corroborates our computed mechanisms.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...