Targeting the tumour microenvironment with an enzyme-responsive drug delivery system for the efficient therapy of breast and pancreatic cancers†
Abstract
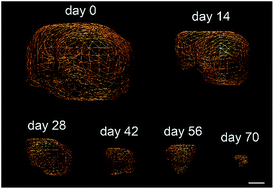
The development of novel therapeutic strategies allowing the destruction of tumour cells while sparing healthy tissues is one of the main challenges of cancer chemotherapy. Here, we report on the design and antitumour activity of a low-molecular-weight drug delivery system programmed for the selective release of the potent monomethylauristatin E in the tumour microenvironment of solid tumours. After intravenous administration, this compound binds covalently to plasmatic albumin through Michael addition, thereby enabling its passive accumulation in tumours where extracellular β-glucuronidase initiates the selective release of the drug. This targeting device produces outstanding therapeutic efficacy on orthotopic triple-negative mammary and pancreatic tumours in mice (50% and 33% of mice with the respective tumours cured), leading to impressive reduction or even disappearance of tumours without inducing side effects.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...