Effect of xylose on the structural and physicochemical properties of peanut isolated protein based films
Abstract
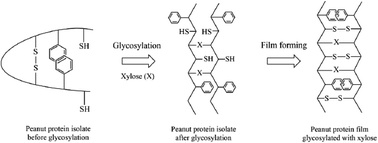
Films based on xylose and peanut protein isolate (PPI) were prepared by solution casting. The effects of xylose content (1%, 2%, 5%, 10%, 20% PPI, w/w) on the structure and mechanical properties of PPI–xylose (PPI–X) film were systematically investigated. The xylose-modified PPI was firstly prepared by crosslinking and modifying of peanut isolated protein with xylose. The degree of glycosylation and surface hydrophobicity significantly increased from 5.6% to 10.9% and from 130.6 to 370.0, respectively, with the increase of the xylose content. Maillard reactions occurring between PPI and xylose were confirmed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Then the xylose-modified PPI was developed into films. PPI–X films showed markedly increased tensile strength (increased by 77%) and elongation (increased by 67%) and decreased solubility (from 96.6% to 43.4%) compared to PPI films, suggesting that the incorporation of xylose could markedly enhance the mechanical properties and the water resistance of films. This property improvement was correlated to the increased protein surface hydrophobicity and sulfhydryl group content with the addition of xylose. No significant differences were detected among L*, a*, b* colour values of all films (P > 0.05). The scanning electron microscope images of the PPI–X film showed that the addition of xylose up to 10% produced a more homogeneous and denser structure. Finally, the improvement mechanism of the PPI–X film was proposed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...