Crack-based strain sensor with diverse metal films by inserting an inter-layer†
Abstract
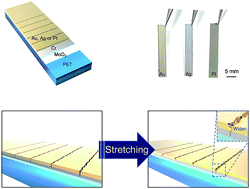
Various sensory systems to detect human motions have been developed for wearable healthcare and artificial electronic skins. Recently, an ultrasensitive mechanical crack-based strain sensor inspired by a spider's slit organ has been proposed. In spite of its high sensitivity, flexibility, and fascinating sensing ability to vibration, the materials that can be used to manufacture the sensor are limited to certain kinds because of the low adhesion between the substrate and a metal film. Therefore, the compatibility of materials with the substrate is a crucial issue in developing a practical sensor system. Here, we present a mechanical crack-based strain sensor with diverse metal (Au, Ag and Pt) films by introducing an inter-layer. Two inter-layers are used; a Cr layer is for generating cracks and MoO3 layer for enhancing the adhesion between the substrate and the metal layer. When cracks are generated on the Cr layer, they are propagated to the conductive metal layers (Au, Ag and Pt). Our crack-based strain sensor exhibited reproducibility and durability with high sensitivity to strain (GF = ∼1600 for Au and Ag layered crack sensors at 2% strain, GF = ∼850 for Pt layered sensor at 2% strain).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...