A spiro-centered thermopolymerizable fluorinated macromonomer: synthesis and conversion to the high performance polymer†
Abstract
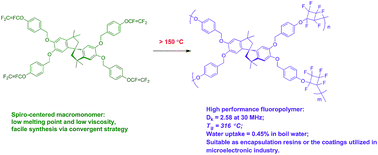
A new spiro-centered thermopolymerizable fluorinated macromonomer is reported here. This four-functional macromonomer is synthesized by a convergent strategy, and shows a low melting point (93 °C) and good solubility in the common organic solvents. When heated to a high temperature, the macromonomer converts into a cross-linked network (PD1), which exhibits a Tg of near 316 °C and a 5% weigh loss at a temperature of 417 °C in N2. PD1 also shows a low dielectric constant (Dk = 2.58 at 30 MHz) and high hydrophobicity (a water contact angle of θ = 98°), as well as low water uptake (about 0.45%, kept in boiling water for 72 h). These results suggest that the macromonomer has a potential application in the production of the high performance polymers, in particular, it is very suitable for encapsulation resins or the coatings utilized in the microelectronics industry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...