Preparation and photoluminescence properties of yellow-emitting CuInS2/ZnS quantum dots embedded in TMAS-derived silica†
Abstract
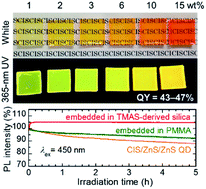
The degradation of CuInS2 (CIS) quantum dots (QDs) under excitation light due to photo-oxidization by O2 has been a significant problem. Embedding QDs into a matrix to protect them against O2 would improve their photostability. In this paper, hydrophilized CIS/ZnS/ZnS QDs prepared by a ligand exchange method were embedded in silica through a sol–gel method using tetramethylammonium silicate (TMAS) aqueous solution, in which negatively-charged nanoparticles can be well dispersed. QDs modified with 3-mercaptopropionic acid (MPA) were well dispersed into TMAS-derived silica. The obtained monolithic TMAS-derived silica composites containing embedded MPA-modified CIS/ZnS/ZnS QDs exhibited high photoluminescence (PL) quantum yields (43–47%). Changes in PL intensity under continuous excitation were measured to evaluate the photostability of the QDs. The PL intensity of the composite was 105% that of the initial value after 5 h irradiation, while the PL intensities of as-prepared QDs and a PMMA composite decreased to 88% and 92%, respectively. The good gas barrier properties of TMAS-derived silica likely caused the high photostability by preventing O2 from reaching the surface of the embedded QDs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...