Lewis acid stabilization and activation of primary N-nitrosamides†
Abstract
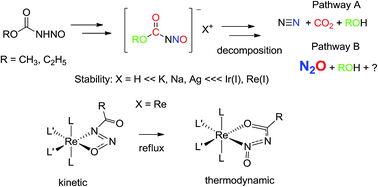
The primary nitrosamides, here exemplified by the N-nitrosoalkylcarbamates, ROC(O)NHNO [R = CH3 (1), R = C2H5 (2)], show a markedly Lewis acid dependent chemistry. Although their alkali metal salts M[ROC(O)NNO] [M = K, R = CH3 (3), M = Na, R = CH3 (3-Na), M = K, R = C2H5 (4), M = Na, R = C2H5 (4-Na)] are stable isolable yellow solids, in solution they undergo pH dependent decomposition to give nitrogen and nitrous oxide as the primary nitrogen containing gaseous products. However chelation to a transition metal, [Re(L)(CO)2(PPh3)2], L = ROC(O)NNO− gives rise to isomeric kinetic and thermodynamic products. Both are thermally stable and together illustrate the stability provided by a chelating low valent transition metal. The preparation, IR, NMR, and X-ray crystallographic characterization of these derivatives are reported. Taken together, these results demonstrate that the Lewis acid identity is an important factor in primary nitrosamide chemistry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...