Ultra-high molecular weight elastomeric polyethylene using an electronically and sterically enhanced nickel catalyst†
Abstract
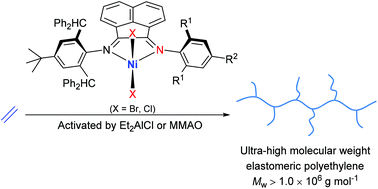
A collection of ten related 1,2-bis(imino)acenaphthene-nickel(II) halide complexes, [1-[2,6-{(C6H5)2CH}2-4-{C(CH3)3}-C6H2N]-2-(ArN)C2C10H6]NiX2 (X = Br: Ar = 2,6-Me2C6H3Ni1, 2,6-Et2C6H3Ni2, 2,6-iPr2C6H3Ni3, 2,4,6-Me3C6H2Ni4, 2,6-Et2-4-MeC6H2Ni5) and (X = Cl: Ar = 2,6-Me2C6H3Ni6, 2,6-Et2C6H3Ni7, 2,6-iPr2C6H3Ni8, 2,4,6-Me3C6H2Ni9, 2,6-Et2-4-MeC6H2Ni10), each bearing one sterically and electronically enhanced N-2,6-dibenzhydryl-4-t-butylphenyl group, have been prepared and fully characterized. The unsymmetrical nature of the chelating bis(imino)acenaphthene is confirmed in the paramagnetic 1H NMR spectra for Ni1–Ni10, while the molecular structures of Ni1, Ni2 and Ni6 highlight the unequal steric protection of the nickel center imposed by their respective N,N-ligands. On activation with either Et2AlCl or MMAO, all the nickel complexes were highly active catalysts in ethylene polymerization [as high as 1.26 × 107 g of PE per mol of Ni per h] affording exceptionally high molecular weight (up to 3.1 × 106 g mol−1) hyper-branched polyethylene. Analysis of the mechanical properties reveals the ultra-high molecular weight polymers possess high tensile strength, excellent shape fixity and elastic recovery (up to 69%) as well as high elongation at break (εb = 843.9%); such materials offer a promising alternative to current thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...