Rapid copolymerization of canola oil derived epoxide monomers with anhydrides and carbon dioxide (CO2)†
Abstract
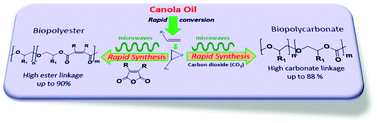
A canola oil derived monomer, 1-decene, was converted to 1,2-epoxydecane with >90% yield. The ring opening copolymerization of 1,2-epoxydecane with carbon dioxide (CO2) and different cyclic anhydrides including maleic, succinic, itaconic, phthalic and tetrahydrophthalic was carried out using a double metal cyanide (DMC) catalyst under microwave and conventional heating conditions. The microwave-assisted polymerizations were significantly faster than those observed under conventional heating conditions. The polycarbonates, copolymers with CO2, were synthesized within minutes (∼30 min) under microwave conditions with high conversions (up to 99%), carbonate linkage (∼88%) and molecular weight (Mw ∼ 15 kDa). The polyesters, copolymers with anhydrides, were synthesized in ∼60 min with high ester content (up to 90%) and Mw (up to 17 kDa). The synthesized copolymers were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR), gel permeation chromatography (GPC), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) techniques. The configuration of double bonds in unsaturated polyesters such as poly(1-decene-co-maleate) was completely isomerized through post polymerization modification to enhance its activity as an unsaturated polyester resin (UPR) for different potential applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...