Effect of epoxy monomer structure on the curing process and thermo-mechanical characteristics of tri-functional epoxy/amine systems: a methodology combining atomistic molecular simulation with experimental analyses†
Abstract
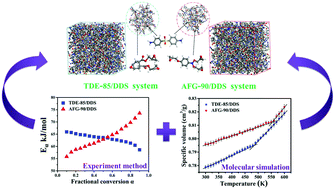
The curing kinetics and thermo-mechanical characteristics of two kinds of high-performance amine cured tri-functional epoxy resin compounds, including diglycidyl-4,5-epoxycyclohexane-1,2-dicarboxylate and N,N-diglycidyl-4-glycidyloxyaniline, were systematically studied herein. Different to the simple bi-functional epoxy resins studied before, the increase in epoxy functionality and resultant asymmetric monomer structure made the whole curing behaviour more difficult to analyse. Nevertheless, there is an urgent demand to provide a thorough understanding of the tri-functional epoxy resin/amine system in order to obtain the desired macro-performance. In this paper, a methodology, which combines atomistic molecular simulation with experimental research, was established to expound the effect of the asymmetric epoxy monomer structure on the reaction kinetics and ultimate performance of the tri-functional epoxy/amine system. It can be utilized to efficiently analyse the cross-linking procedure and the microstructure–property relationships of epoxy resin with poly-functionality and asymmetric monomer structures, thereby serving as guidance to design high-performance polymer matrices for advanced composites.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...