Enhancing a long-range salt bridge with intermediate aromatic and nonpolar amino acids†
Abstract
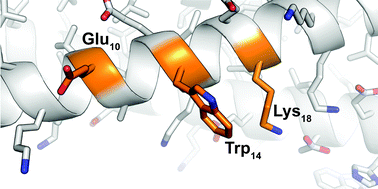
The interaction of a positively charged amino acid residue with a negatively charged residue (i.e. a salt bridge) can contribute substantially to protein conformational stability, especially when two ionic groups are in close proximity. At longer distances, this stabilizing effect tends to drop off precipitously. However, several lines of evidence suggest that salt-bridge interaction could persist at longer distances if an aromatic amino acid residue were positioned between the anion and cation. Here we explore this possibility in the context of a peptide in which a Lys residue occupies the i + 8 position relative to an i-position Glu on the solvent-exposed surface of a helix-bundle homotrimer. Variable temperature circular dichroism (CD) experiments indicate that an i + 4-position Trp enables a favorable long-range interaction between Glu and the i + 8 Lys. A substantial portion of this effect relies on the presence of a hydrogen-bond donor on the arene; however, non-polar arenes, a cyclic hydrocarbon, and an acyclic Leu side-chain can also enhance the long-range salt bridge, possibly by excluding water and ions from the space between Glu and Lys.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...