Contacts to solution-synthesized SnS nanoribbons: dependence of barrier height on metal work function†
Abstract
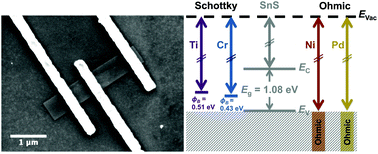
Tin(II) monosulfide (SnS) is a layered, anisotropic material that is of interest as a two-dimensional semiconductor for opto-electronic, thermoelectric, and piezoelectric applications. In this study, the effect of work function on contact behavior was investigated. Ni/Au, Pd/Au, Cr/Au, and Ti/Au contacts were fabricated onto individual, solution-synthesized, p-type SnS nanoribbons. The lower work function metals (Cr and Ti) formed Schottky contacts, whereas the higher work function metals (Ni and Pd) formed ohmic or semi-ohmic contacts. Of the ohmic contacts, Ni was found to have a lower contact resistance (∼10−4 Ω cm2 or lower) than Pd (∼10−3 Ω cm2 or lower). Both the calculated Schottky barriers (0.39 and 0.50 eV) for Cr and Ti, respectively, and the ohmic behavior for Ni and Pd agree with behavior predicted by Schottky–Mott theory. The results indicate that high work function metals should be considered to form low resistance contacts to SnS multilayers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...