Solute particle near a nanopore: influence of size and surface properties on the solvent-mediated forces†
Abstract
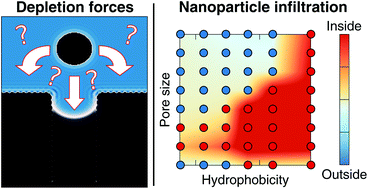
Nanoscopic pores are used in various systems to attract nanoparticles. In general the behaviour is a result of two types of interactions: the material specific affinity and the solvent-mediated influence also called the depletion force. The latter is more universal but also much more complex to understand since it requires modeling both the nanoparticle and the solvent. Here, we employed classical density functional theory to determine the forces acting on a nanoparticle near a nanoscopic pore as a function of its hydrophobicity and its size. A simple capillary model is constructed to predict those depletion forces for various surface properties. For a nanoscopic pore, complexity arises from both the specific geometry and the fact that hydrophobic pores are not necessarily filled with liquid. Taking all of these effects into account and including electrostatic effects, we establish a phase diagram describing the entrance and the rejection of the nanoparticle from the pore.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...