Lithiation-assisted exfoliation and reduction of SnS2 to SnS decorated on lithium-integrated graphene for efficient energy storage†
Abstract
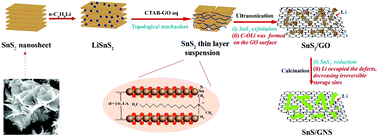
Low reversion of lithium sulfide and defects causing irreversible capacity loss are the primary causes of low Coulombic efficiency in tin sulfide/graphene-based composites. Herein, we synthesized a SnS/graphene composite via a novel lithiation-assisted exfoliation and reduction method using SnS2, n-butyllithium, and graphene oxide as raw materials. The experimental results reveal that lithium from the insertion agent combine with the oxygen-containing groups on graphene oxide; this can help in the reduction of hexagonal SnS2 to orthorhombic SnS during calcination and simultaneous pre-occupancy of the edge and defect sites of graphene; thus, additional lithium ion consumption during the initial several lithiation processes is diminished. Microstructural characterizations indicate that the exfoliated SnS nanosheets with a dramatically decreased lateral size (50–100 nm) are uniformly decorated on the surface of lithium-integrated graphene sheets. Consequently, the as-prepared SnS/graphene composite exhibits a significantly high SnS ultilization with a 77.5% initial Coulombic efficiency, which is the highest value reported in the current literature. Moreover, an excellent reversibility of conversion reaction (SnS + 2Li+ + 2e− ↔ Sn + Li2S) and a high reversible capacity of 1016.4 mA h g−1 after 100 cycles are expressed in this composite electrode, demonstrating its importance as an anode material for energy storage.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...