One dimensional building blocks for molecular separation: laminated graphitic nanoribbons†
Abstract
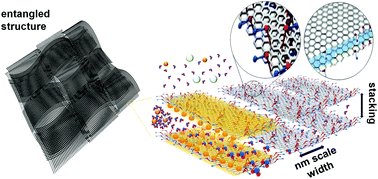
Herein, a new carbon-based graphitic membrane composed of laminated graphitic nanoribbons with a nanometer-scale width and micrometer-scale length, the graphitic nanoribbon membrane, is reported. Compared to the existing graphitic membranes, such as those composed of graphene oxide and carbon nanotubes, the developed membrane exhibits several unique characteristics in pressure-driven systems. First, the short diffusion length through its interlayer and the free volume of its stacked nanoribbons result in high solvent flux regardless of solvent polarity (water: 25–250 L m−2 h−1 bar−1; toluene: ∼975 L m−2 h−1 bar−1; hexane: ∼240 L m−2 h−1 bar−1). The flux value for water is one order of magnitude higher, while that for nonpolar organic solvents is two to three orders of magnitude greater than the corresponding flux values obtained through commercially available nanofiltration membranes. Second, the membrane exhibits good separation performance, particularly with organic dye molecules (∼100%) and trivalent ions (∼60%), maintaining high solvent flux during extended filtration. Finally, the membrane exhibits high stability in various fluids, e.g., 1 M HCl solution, 1 M NaOH solution, toluene, ethanol, and water, as well as under hydraulic pressures of up to 50 bar. Electron microscopy observation and simulation results suggest that such distinctive features of the membrane are related to the entangled thin multilayers of the graphitic nanoribbons, which possibly originate from the high aspect ratio and narrow width of the nanoribbons.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...