Hybrid nanomaterials of WS2 or MoS2 nanosheets with liposomes: biointerfaces and multiplexed drug delivery†
Abstract
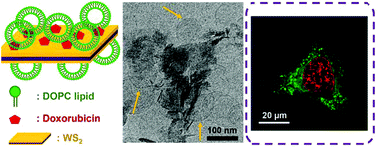
Lipid containing hybrid materials are of significant interest for biointerface research and drug delivery applications, and a large number of previous studies have focused on graphene oxide (GO). In this work, novel hybrid materials made of transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs) and phosphocholine (DOPC) liposomes were prepared and compared with GO. All these inorganic materials are 2D nanosheets. DOPC liposomes are adsorbed by tungsten disulfide (WS2) as intact liposomes as indicated by cryo-TEM and liposome leakage assays. WS2 likely uses van der Waals forces for liposome adsorption as determined from urea, salt, and surfactant washing experiments. In addition, WS2 adsorbed doxorubicin (DOX) and DOPC liposomes synergistically. The adsorption capacity of DOPC on bare WS2 was 22.5% of the weight of WS2. After adsorbing DOX on WS2, the liposome adsorption capacity increased to ∼110%. Hydrogen bonding also contributed to liposome adsorption on DOX-loaded WS2. Confocal fluorescence microscopy confirmed the uptake of the DOPC/WS2 hybrid material by HeLa cells, and the co-delivery of DOX and calcein was achieved by loading calcein inside the liposomes. This study provides fundamental insights into the interaction between PC liposomes and WS2. Furthermore, preliminary biomedical applications of this hybrid material were explored.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...