A highly controllable protein self-assembly system with morphological versatility induced by reengineered host–guest interactions†
Abstract
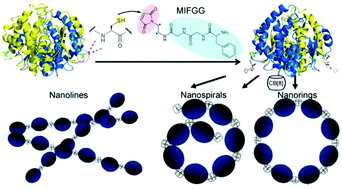
Manipulating proteins to self-assemble into highly ordered nanostructures not only provides insights into the natural protein assembly process but also allows access to advanced biomaterials. Host–guest interactions have been widely used in the construction of artificial protein assemblies in recent years. CB[8] can selectively associate with two tripeptide Phe-Gly-Gly (FGG) tags with an extraordinarily high binding affinity (Kter = 1.5 × 1011 M−2). However, the FGG tags utilized before are all fixed to the N-termini via genetic fusion; this spatial limitation greatly confined the availability of the CB[8]/FGG pair in the construction of more sophisticated protein nanostructures. Here we first designed and synthesized a maleimide-functionalized Phe-Gly-Gly tag as a versatile site-specific protein modification tool; this designed tag can site-selectively introduce desired guest moieties onto protein surfaces for host–guest driven protein assembly. When regulating the self-assembly process of proteins and CB[8], the constructed protein nanosystem can exhibit distinctive morphological diversities ranging from nanorings, nanospirals, nanowires to superwires. This work developed a new strategy for site-specific protein modification of the CB[8] binding tag and provides a possible direction for the construction of ‘smart’, dynamic self-assembly systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...