Platinum nanowires anchored on graphene-supported platinum nanoparticles as a highly active electrocatalyst towards glucose oxidation for fuel cell applications
Abstract
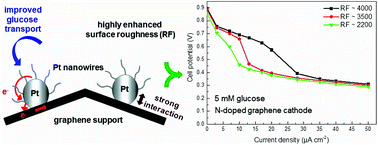
The limited performance of platinum-based electrocatalysts for glucose electrooxidation is a major concern for glucose fuel cells, since glucose electrooxidation is characterized by slow reaction kinetics and low diffusion coefficient. Here, the presented graphene-supported platinum-based hierarchical nanostructures attain highly enhanced electrocatalytic activity towards glucose oxidation. Platinum nanoparticles electrodeposited on graphene support retain mechanical stability and act as junctions allowing a reliable, smooth and dense growth of platinum nanowires with extremely small diameters (>10 nm) on graphene. The electrode's surface roughness was increased by factors up to 4000 to the geometrical surface area enabling maximized exploitation of the electrocatalytic activity of platinum and efficient electron transfer between nanowires and the substrate. The unique three-dimensional geometry of these hierarchical nanostructures has a significant impact on their catalytic performance offering short diffusional paths for slow glucose species, thus, mass transport limitations are optimized leading to lower polarization losses. This was examined by galvanostatic measurements of the operation as anodes in glucose half-cells under conditions corresponding to implantable glucose fuel cells. The presented hierarchical nanostructures show remarkably enhanced catalytic performance for glucose electrooxidation, i.e. a negatively shifted open circuit potential of −580 mV vs. Ag/AgCl, hence, representing appropriate electrocatalysts for use as anodes in glucose fuel cells. In combination with a non-metal N-doped graphene cathode, a cell potential of 0.65 V was achieved at a galvanostatic load of 17.5 μA cm−2 which noticeably surpasses the performance of state of the art catalysts for the aforementioned operation conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...