Photocatalytic photosystem I/PEDOT composite films prepared by vapor-phase polymerization†
Abstract
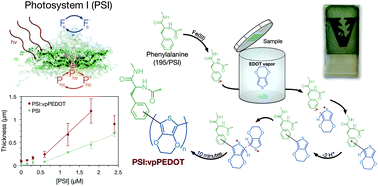
Photosystem I (PSI) achieves photo-induced charge separation with outstanding internal quantum efficiency and has been used to improve the performance of various photoelectrochemical systems. Herein, we describe a fast and versatile technique to assemble composite films containing PSI and a chosen intrinsically conductive polymer (ICP). A mixture of PSI and a Friedel–Crafts catalyst (FeCl3) is drop cast atop a substrate of choice. Contact with ICP monomer vapor at low temperature stimulates polymer growth throughout PSI films in minutes. We assess the effects of PSI loading on the rapid vapor-phase growth of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) within and above PSI multilayer films, and characterize the resulting film's thickness, electrochemical capacitance, and photocatalytic response. Composite films generate cathodic photocurrent when in contact with an aqueous redox electrolyte, confirming retention of the photocatalytic activity of the polymer-entrapped PSI multilayer assembly.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...