Bushy sphere dendrites with husk-shaped branches axially spreading out from the core for photo-catalytic oxidation/remediation of toxins†
Abstract
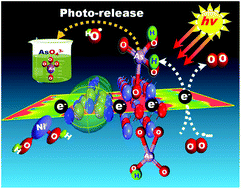
This work describes densely interlinked bushy “tree-like chains” characterized by neatly branched sphere dendrites (bushy sphere dendrites, BSD) with long fan-like, husk-shaped branching paths that extend longitudinally from the core axis of the {110}-exposed plane. We confirmed that the hierarchical dendrite surfaces created bowls of swirled caves along the tree-tube in the mat-like branches. These surfaces had high-index catalytic site facets associated with the formation of ridges/defects on the dominant {110}-top-cover surface. These swirled caves along the branches were completely filled with 50–100 nm poly-CN nano-sphere-fossils with orb-like appearance. Such structural features are key issues of the inherent surface reactivity of a powerful catalyst/trapper, enabling photocatalytic oxidation and trapping of extremely toxic arsenite (AsO33−) species and photo-induced recovery of arsenate (AsO43−) products from catalyst surfaces. The light-induced release of produced AsO43− from BSD indicates (i) highly controlled waste collection/management (i.e., recovery), (ii) low cost and ecofriendly photo-adsorbent, (iii) selective trapping of real sample water to produce water-free arsenite species; (iv) multiple reuse cycles of catalysts (i.e., reduced waste volume). Matrixed dendrites, covered with 3D microscopic sphere cores that capture solar-light, trap toxins, and are triggered by light, were designed. These dendrites can withstand indoor and outdoor recovery of toxins from water sources.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...