Osmotin-loaded magnetic nanoparticles with electromagnetic guidance for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease†
Abstract
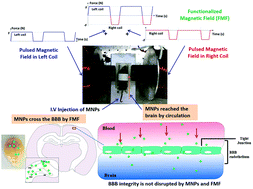
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most prevalent age-related neurodegenerative disease, pathologically characterized by the accumulation of aggregated amyloid beta (Aβ) in the brain. Here, we describe for the first time the development of a new, pioneering nanotechnology-based drug delivery approach for potential therapies for neurodegenerative diseases, particularly AD. We demonstrated the delivery of fluorescent carboxyl magnetic Nile Red particles (FMNPs) to the brains of normal mice using a functionalized magnetic field (FMF) composed of positive- and negative-pulsed magnetic fields generated by electromagnetic coils. The FMNPs successfully reached the brain in a few minutes and showed evidence of blood–brain barrier (BBB) crossing. Moreover, the best FMF conditions were found for inducing the FMNPs to reach the cortex and hippocampus regions. Under the same FMF conditions, dextran-coated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) loaded with osmotin (OMNP) were transported to the brains of Aβ1–42-treated mice. Compared with native osmotin, the OMNP potently attenuates Aβ1–42-induced synaptic deficits, Aβ accumulation, BACE-1 expression and tau hyperphosphorylation. This magnetic drug delivery approach can be extended to preclinical and clinical use and may advance the chances of success in the treatment of neurological disorders like AD in the future.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...