The size-effect of gold nanoparticles and nanoclusters in the inhibition of amyloid-β fibrillation†
Abstract
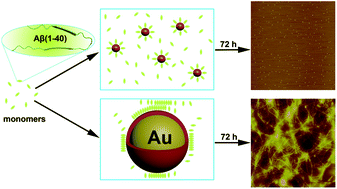
A significant pathological signature of Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the deposition of amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques in the brain and the synaptic dysfunction and neurodegeneration associated with it. Compounds or drugs that inhibit Aβ fibrillation are thus desirable to develop novel therapeutic strategies against AD. Conventional strategies usually require an elaborate design of their molecular structures. Here we report the size-effect of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) and nanoclusters (AuNCs) in the inhibition of protein amyloidosis. Using L-glutathione stabilized AuNPs with different sizes and AuNCs as examples, we show that large AuNPs accelerate Aβ fibrillation, whereas small AuNPs significantly suppress this process. More interestingly, AuNCs with smaller sizes can completely inhibit amyloidosis. Dynamic light scattering (DLS) experiments show that AuNCs can efficiently prevent Aβ peptides from aggregation to larger oligomers (e.g. micelles) and thus avoid nucleation to form fibrils. This is crucially important for developing novel AD therapies because oligomers are the main source of Aβ toxicity. This work presents a novel strategy to design anti-amyloidosis drugs, which also provides interesting insights to understand how biological nanostructures participate in vivo in Aβ fibrillation from a new perspective.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...