Integration of stem cell-derived exosomes with in situ hydrogel glue as a promising tissue patch for articular cartilage regeneration†
Abstract
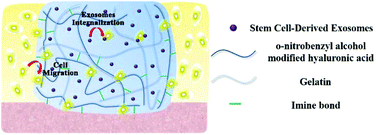
The regeneration of articular cartilage, which scarcely shows innate self-healing ability, is a great challenge in clinical treatment. Stem cell-derived exosomes (SC-Exos), an important type of extracellular nanovesicle, exhibit great potential for cartilage regeneration to replace stem cell-based therapy. Cartilage regeneration often takes a relatively long time and there is currently no effective administration method to durably retain exosomes at cartilage defect sites to effectively exert their reparative effect. Therefore, in this study, we exploited a photoinduced imine crosslinking hydrogel glue, which presents excellent operation ability, biocompatibility and most importantly, cartilage-integration, as an exosome scaffold to prepare an acellular tissue patch (EHG) for cartilage regeneration. It was found that EHG can retain SC-Exos and positively regulate both chondrocytes and hBMSCs in vitro. Furthermore, EHG can integrate with native cartilage matrix and promote cell deposition at cartilage defect sites, finally resulting in the promotion of cartilage defect repair. The EHG tissue patch therefore provides a novel, cell-free scaffold material for wound repair.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...