Contactless near-field scanning thermoreflectance imaging†
Abstract
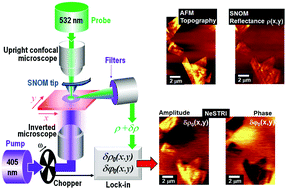
Determining and imaging the thermal properties at the nanoscale is a demanding experimental challenge. So far, virtually any techniques used to image nanoscale thermal properties require to position the sample in contact with voluminous probes that act as undesirable thermal sinks and dramatically affect the measurements, in spite of poor interfacial thermal resistivity. Thermoreflectance, a contactless technique in which thermal conductivity is measured by optically probing the heat-induced changes in a sample, is extensively used for measuring the macroscopic and microscopic thermal properties of solids, but, so far, has been limited by diffraction in its applicability at the nanoscale. Here, we present near-field scanning thermoreflectance imaging (NeSTRI), a new scanning probe technique in which an aperture-type near-field optical microscope at sub-wavelength resolution is used to contactlessly determine the thermoreflectance of thin films. As a case study, NeSTRI is here applied to multilayer graphene thin films on glass substrates. Thermal conductivity of micrometre-size multilayer graphene platelets is determined and is consistent with previous macroscopic predictions. We also find that the thermal conductivity is locally higher at specific crystallographic edges of multilayer graphene platelets, which is indicative of the spatial resolution of our method. NeSTRI is uniquely suited to understanding the thermal properties of a large class of nanostructured and nanoscale systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...