The roles of surface chemistry, dissolution rate, and delivered dose in the cytotoxicity of copper nanoparticles†
Abstract
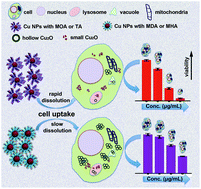
The understanding of nanoparticle (NP) cytotoxicity is challenging because of incomplete information about physicochemical changes particles undergo once they come into contact with biological fluids. It is therefore essential to characterize changes in NP properties to better understand their biological fate and effects in mammalian cells. In this paper, we present a study on the effect of particle surface oxidation and dissolution rates of Cu NPs. Particle dissolution, cell-associated Cu doses, and oxidative stress responses in A549 luciferase reporter cells were examined for Cu NPs modified with mercaptocarboxylic acids with different carbon chain lengths and a thiotic acid appended-PEG ligand (TA). We found that these Cu NPs released ionic species together with small particles upon oxidation and that surface chemistry influenced the morphology and dissolution rate. The dissolution rate was also shown to impact both the cellular Cu dosimetry and associated oxidative stress responses. The convergent results from dissolution and dosimetry measurements demonstrate that both intracellular and extracellular (i.e., NP uptake-independent) release of ionic species from Cu NPs greatly affect the cytotoxicity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...