Electrically controlled release of insulin using polypyrrole nanoparticles†
Abstract
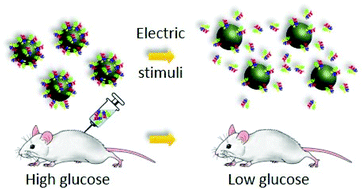
Conducting polymers present an opportunity for developing programmable, adjustable, spatially, and temporally controllable drug delivery systems. While several small molecule drugs have been released from thin conductive polymeric films successfully, delivering large molecule therapeutics, such as polypeptides and nucleic acids, has remained a significant challenge. Poor drug loading (∼ng cm−2) of thin films coupled with film instability has, in many cases, made conducting polymer films refractory to clinical development. To address these limitations, we have utilized conductive polymer nanoparticulate backbones to controllably release insulin, a high molecular weight, clinically relevant polypeptide. We find that the interaction between insulin and the polymer scaffold can be described by a simple Langmuir-type adsorption model. By modifying the ratio of the amount of nanoparticles to the amount of insulin, we have obtained drug loading percentages estimated to be as high as 51 wt% percent. In vivo experiments in mice confirmed retained bioactivity of the released insulin after electrical stimulation.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 Nanoscale HOT Article Collection

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...