Highly recyclable Ag NPs/alginate composite beads prepared via one-pot encapsulation method for efficient continuous reduction of p-nitrophenol†
Abstract
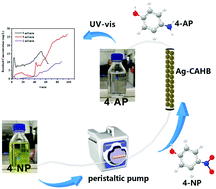
Nanosilver/alginate composite beads were successfully fabricated via a simple one-pot encapsulation method and were effectively applied to degradation experiments with p-nitrophenol under batch and fixed-bed conditions. Three-dimensional alginate hydrogels cross-linked with calcium ions were used as supporting matrix for “confinement” of the nanosilver, leading to the formation of nanosilver/alginate composite beads without significant aggregation of active nanoparticles. The samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. As-fabricated bead-like samples showed excellent catalytic efficiency at ambient temperature; material with 10% silver content required 170 seconds to catalyze hydrogenation of highly toxic p-nitrophenol under batch conditions. Good stability was also demonstrated in the process of dynamic catalytic degradation, which showed continuous high conversion performance for 4-NP; about 40 minutes at 298 K and residual concentration reached 0.0335 mg L−1 at a flow rate of 1 mL min−1. A pseudo-first order kinetic model described the relationship between concentration and time well; the rate constant k is 0.0149 s−1. Very favorably, the way to recycle the catalyst is very simple, namely filtration only is enough. In addition, the catalytic capability did not decline significantly after 10 recycles and average conversion content was still 97.96%.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...