Enhanced catalytic activity and stability of copper and nitrogen doped titania nanorod supported Pt electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction in polymer electrolyte fuel cells†
Abstract
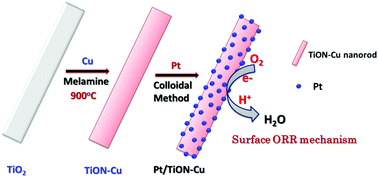
A durable and stable nanostructure consisting of a copper and nitrogen co-doped titania (TiON–Cu 2) nanorod supported catalyst is prepared for polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Pt deposited on TiON–Cu 2 nanorods as a framework in acidic medium exhibits superior mass and specific activity towards the ORR. The Pt loading, relative humidity, and back pressure also influence the overall polymer electrolyte fuel cell (PEFC) performance. In addition, a PEFC comprising TiON–Cu 2 supported Pt as cathode catalyst operated under dry conditions shows a stable current at 0.6 V even up to 100 h. The accelerated stress test (AST-1) for electrocatalyst stability evaluation shows that Pt/C retains 40% of its initial electrochemical surface area (ECSA) after 1000 potential cycles from 1 to 1.5 V vs. DHE, whereas Pt/TiON–Cu 2 retains 55% of its initial catalytic activity and ECSA even after 6000 potential cycles. In addition, the accelerated catalyst durability (AST-2) test for Pt catalyst durability shows that the Pt/TiON–Cu 2 nanorod interaction is sustained even after 18 000 potential cycles between 0.6 and 1.0 V under PEFC operating conditions, and the catalyst retains 75% of its initial ECSA. After the AST, the samples were characterized for further analysis to obtain an insight into their degradation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...