Polyol asserted hydrothermal synthesis of SnO2 nanoparticles for the fast adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue cationic dye†
Abstract
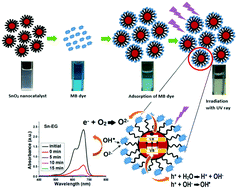
Methylene blue (MB), a toxic dye, is predominantly used in various industries. It is environmentally hazardous and harmful to human beings and aquatic species. Catalyst nanoparticles (NPs) play an important role in the remediation of MB dye. Herein, we report the fast adsorption and efficient degradation of MB dye using nanostructured SnO2 catalysts prepared in various glycol solvents, such as ethylene glycol (EG), diethylene glycol (DEG), tetraethylene glycol (TEG), polyethylene glycol 400 (PEG4) and polyethylene glycol 600 (PEG6). The XRD patterns reveal the formation of the pristine rutile phase of SnO2 with average crystallite sizes from 2 to 3.5 nm with respect to the molecular weight of the polyol solvent used. The use of polymeric glycols of various molecular weights provides a variation in the morphology of the SnO2 catalysts with different specific surface area and active sites owing to the difference in chemical reactivity. Quantum confinement effect and defect bands were observed in the optical spectrum of the SnO2 nanostructures due to the presence of oxygen vacancies or interstitial tin. The nanomaterials possess a high colloidal stability with a negative zeta potential value of more than 30 mV. The above mentioned physical and chemical properties have a significant catalytic effect towards the adsorption (max ∼73%) and degradation (max ∼97%) of MB dye. The negative zeta potential due to polyol functionalization, smaller particle size and high specific surface area of the SnO2 NPs possess the additional advantage of the ultra-fast adsorption of MB cationic dye. Different isotherm models are discussed for the experimental equilibrium data and well fitted with the Langmuir model, which confirmed the monolayer adsorption of dye on the SnO2 surface. In addition, various physiochemical parameters such as the pH of the dye solution, catalyst dosage and the wavelength of the light irradiation were studied and the recyclability of the catalysts was verified. The catalysts also demonstrate significant photodegradation ability for rose bengal anionic dye.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...